Direct printing
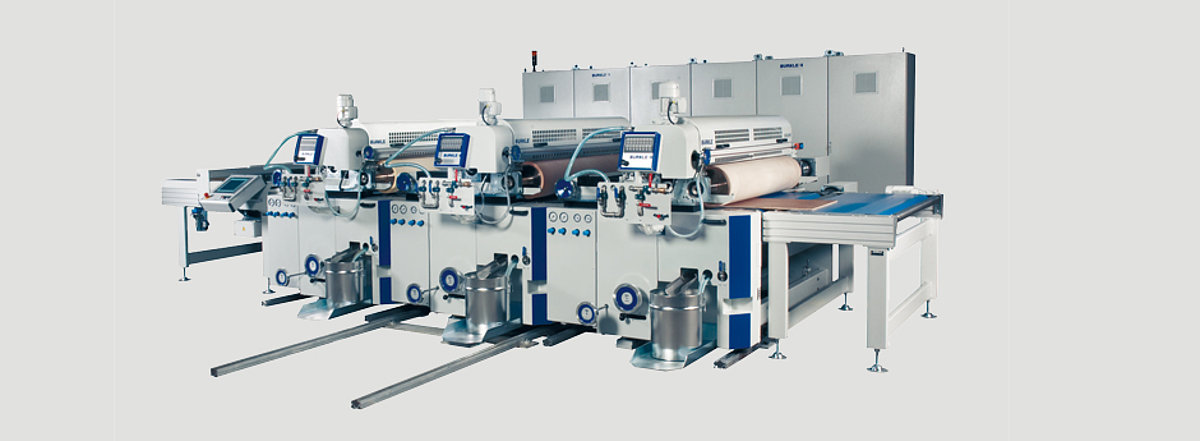
So-called direct printing on panels is a special technology for the refinement of wood surfaces. The ink is applied directly to the wood, not to a substrate that is then glued or pressed onto the wood, as is the case with decor printing. However, there is one crucial difference compared with gravure printing: rather than printing from gravure cylinders, the ink is applied to a blanket cylinder and transferred from there onto the wood.
Due to this amended printing process, the ink must demonstrate a different transfer behaviour. It needs to be transferred from the gravure cylinder to the blanket cylinder without bleeding or drying. Only this will ensure the desired print image is transferred accurately onto the wood surface.
New direct printing machines have working widths of from 720 to 2,500mm and repeat lengths of up to 1,500mm. Feed rates can reach up to 120m/min.
To make a wood structure look authentic in direct printing, the carrier board, usually HDF, must undergo a multistep coating process in which various pigmented, water-dilutable primers are used.
First the raw material is treated with a primer and sanded. Then two undercoats are applied for optimal priming of the surface for printing. Now the one, two or three-colour wood structure can be printed using the direct printing method. To harden the surface, special anti-abrasive undercoats, e.g. UV aluminium oxide lacquer, are applied using the roller method. Before the surface is finally varnished, it has to be thoroughly sanded again. Using a laser-cut rubber roller, an additional tactile lacquer can be applied either synchronously or asynchronously to the wood structure for even closer approximation of the surface of the natural wood structure.